What are Martensitic Ceramic Blow Bars?
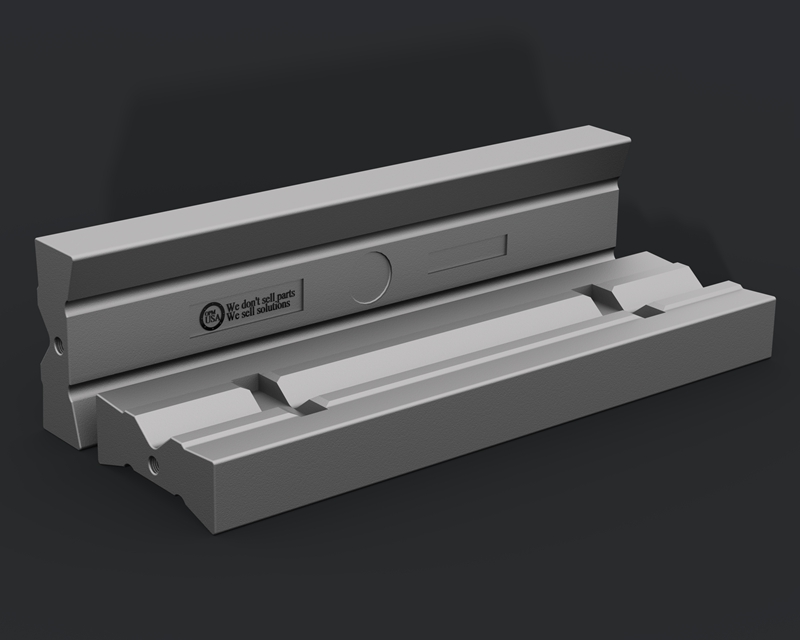
Martensitic Ceramic blow bars are blow bars of martensitic steel with ceramic inlays. They are the most critical wear and tear part of impact crushers. It mainly crushes limestone, concrete, and asphalt. Blow bars or impact hammers with ceramic inserts are a significant development for aggregate crushing operations.
This alloy offers almost similar resistance to impact as manganese steel but higher resistance to abrasion wear. It is recommended for primary crushing and medium-low abrasiveness recycling.
While the martensitic alloy is highly impact-resistant, the ceramic inlays, on the other hand, improve abrasion resistance. Crushers that use concrete recycling and primary crushing applications use such combinations.
Material of Martensitic Ceramic Blow Bars
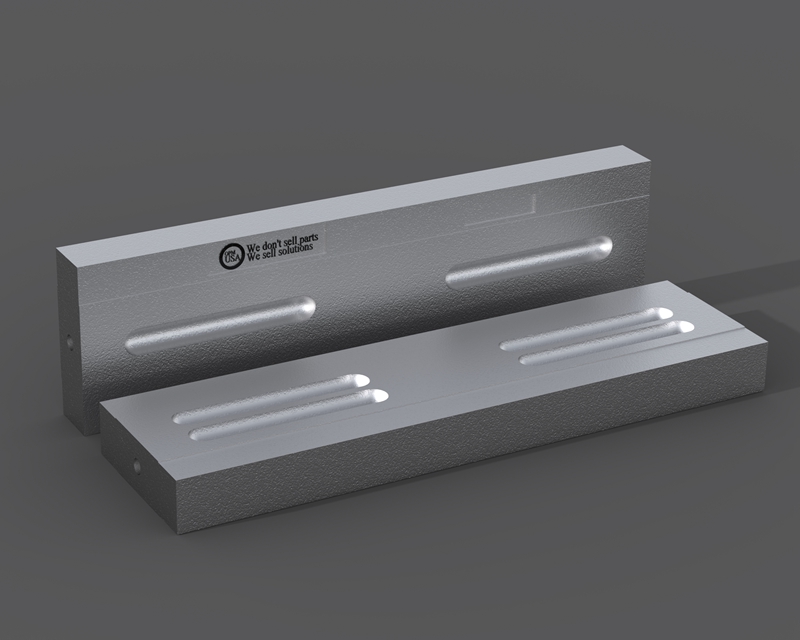
Our engineers have explicitly modeled and designed martensitic steel with a ceramic matrix. It is to integrate the highest abrasiveness throughout the bar. This bar benefits from our standard martensitic with the added wear resistance of ceramics inlay.
Additionally, It also increases blow bars’ longevity and service life. When combined with ceramic inserts, Martensitic steel alloy dramatically increases the blow bars’ lifetime by almost 100%.
The martensitic ceramic mixture is typically used in primary and recycling applications, usually where a medium abrasive material is crushed. As one of the finest alloy combinations, this alloy would only tolerate small feed sizes.
Benefits of Using Martensitic Steel
Martensite is an entirely carbon-saturated iron type made by quick cooling-off. A heat treatment removes carbon from the martensite to improve its strength and wear properties.
When inserted with high-hardness ceramics, the martensitic steel blow bar is dramatically enforced for wear resistance on the wear surface.
This makes them the ideal solutions for primary or secondary crushing where wear and impact resistance are required. The lifetime is doubled or longer on martensitic blow bars without ceramic inserts.
The high abrasion resistance has been reported to operate for extended periods of crushing when compared to monometallic blow bars.